Our team paper is updated on the projects page and see the project detail there.
1) Firstly, the link between paper influence and authors influence is biased.
a) Innovative researcher may get shadowed by limited productivity originated from their large efforts on individual paper. A typical scenario would be a founding scientist who had three thousand-citing paper but only obtained an H-index of 3. The quantity of his work will offsets the profundity. Only the authors with a large number of papers with high citation will be recognized.
b) Innovative researcher will be shadowed by the limited number of journals in his field. The typical scenario is a scientist in biology and information science could easily obtain a H-index over 10, which is hard for a mathematician and theoretical physicist. Networking effect should be normalized.
c) Though paper published on prestigious journals usually gain more citations, the varied significance of publicationfrom different journals still remain not well accounted for. Especially for those innovative authors who usually publish on high rated journals gain same citation.
d) The author’s active contribution is not indicated in the H-index. Innovative author placed as the first author gain the same citation number as the second author.
e)On the connectivity side, the index say nothing about the cooperation of scholars. Such cooperation indicates the potential of innovation and the spread of academic findings
2) Secondly, the influence of paper measured by the citation number is biased.
a) Citations do not account for confounding factors such as "gratuitous authorship", the so-called Matthew effect, and the favorable citation bias associated with review articles. Again, this is a problem for all other metrics using publications or citations.
Looks like using network influence is better!
1) Firstly, the link between paper influence and authors influence is biased.
a) Innovative researcher may get shadowed by limited productivity originated from their large efforts on individual paper. A typical scenario would be a founding scientist who had three thousand-citing paper but only obtained an H-index of 3. The quantity of his work will offsets the profundity. Only the authors with a large number of papers with high citation will be recognized.
b) Innovative researcher will be shadowed by the limited number of journals in his field. The typical scenario is a scientist in biology and information science could easily obtain a H-index over 10, which is hard for a mathematician and theoretical physicist. Networking effect should be normalized.
c) Though paper published on prestigious journals usually gain more citations, the varied significance of publicationfrom different journals still remain not well accounted for. Especially for those innovative authors who usually publish on high rated journals gain same citation.
d) The author’s active contribution is not indicated in the H-index. Innovative author placed as the first author gain the same citation number as the second author.
e)On the connectivity side, the index say nothing about the cooperation of scholars. Such cooperation indicates the potential of innovation and the spread of academic findings
2) Secondly, the influence of paper measured by the citation number is biased.
a) Citations do not account for confounding factors such as "gratuitous authorship", the so-called Matthew effect, and the favorable citation bias associated with review articles. Again, this is a problem for all other metrics using publications or citations.
Looks like using network influence is better!
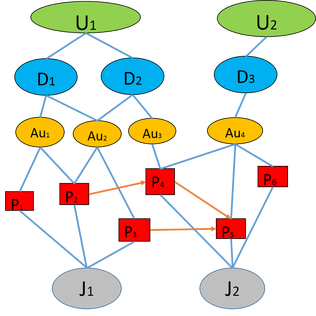
Our final model of analyzing the paper-paper citation network and paper-academic entity network (entities include the author, departments, universities and journals).
For computing concern, we split the network and analyze it step-by-step.
We utilized PageRank, HITS algorithm to calculate the network centrality, authority and connectivity.
To be updated...
For computing concern, we split the network and analyze it step-by-step.
We utilized PageRank, HITS algorithm to calculate the network centrality, authority and connectivity.
To be updated...
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
